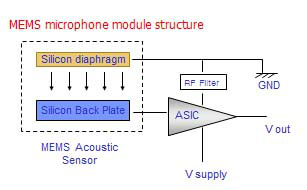
The MEMS microphone stands for Microphone Electronics Mechanical System. As with other microphones, the sound pressure is converted into electrical signals.
Depending on the design, the sound signal is converted into a corresponding analog output voltage or into a digital pulse density modulated (PDM) output signal.
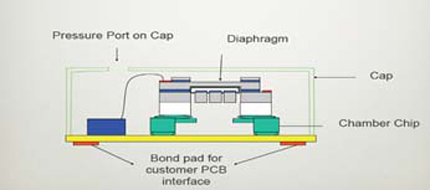
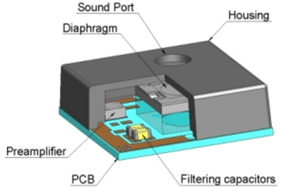
Sound is converted into electrical signals by changing the coupling capacitance between a fixed base plate and a movable base plate (diaphragm).
The sound hits the membrane and sets it in motion. This changes the air gap and thus the capacitance between the base plate and the diaphragm plate.
The compressed air in the rear chamber can escape through the pressure equalization opening, allowing the diaphragm to move. The electrical signals are then amplified by an ASIC chip.
An omnidirectional or unidirectional microphone directional characteristic is achieved by using appropriate RF noise suppression filters.
Some microphones are designed with the opening at the top of the housing or at the bottom of the circuit board.
The advantages of a MEMS microphone
- High sensitivity of up to -26 dB
- Signal-to-noise ratio > 60 dB
- Small design of approx. 3x4mm and 1mm height
- Reflow solderable
- SMD mountable
- Wide temperature range from -40°C to +100°C